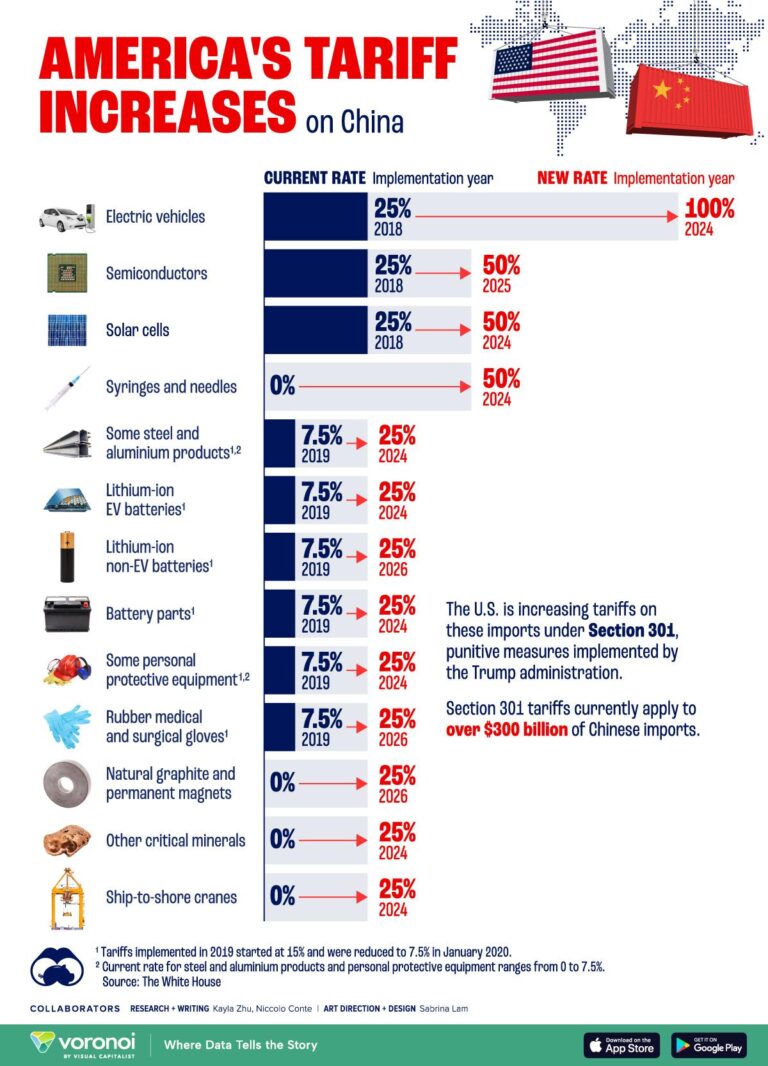
In a significant shiftŌüó in U.S. trade policy, former President Donald Trump’s recent executive order threatens toŌĆŹ impose tariffs of at leastŌĆī 54 percent Ōüóon aŌüż wide range of Chinese imports. This bold move aims to challenge China’s tradeŌĆŹ practices and address concerns over intellectual propertyŌĆī theft and unfair competitive advantages. The potential tariffs, reported by The New ŌĆīYorkŌüó Times, could have far-reaching implications not only for bilateral trade Ōüórelations but also for global markets and supply chains. As tensionsŌüŻ escalate between theŌüż two economic superpowers, this article delves into the details of the newŌüż tariff order, its anticipated impact on the Chinese economy, and the broader consequences for ŌĆŗconsumers and businesses worldwide.
Impact of Tariffs ŌĆŗon ŌĆŗChina’s Economy and Manufacturing Sector
The imposition ofŌĆī tariffsŌüż at ŌĆŗa staggering 54 percent represents a seismic shift in theŌüó trade dynamics between the United States and China, especiallyŌĆŗ for the latter’s economy and manufacturing sector. ŌĆŹAs the cornerstone of ŌüóChina’s growth over recent decades, the manufacturing industry Ōüżfaces significantŌüó challengesŌĆŗ inŌĆī maintaining itsŌüż competitive edge. A ŌüŻsurgeŌüż in operational costs due to elevatedŌüŻ tariffs compels manufacturers to rethink their Ōüżsupply chains, possibly Ōüóleading to a reduction in production capacity and the realignmentŌĆŹ of sourcing materials. Key outcomesŌĆŹ may include:
- Increased Prices: The ŌĆŹhigher tariffs are ŌüŻlikely to be passed onto ŌüŻconsumers, resulting Ōüżin inflated ŌĆīprices for goods.
- Supply Chain Disruption: Companies may seek alternative suppliers outside of China, leading to a Ōüżpotential decoupling of established business relationships.
- job Losses: As Ōüóproduction shifts, aŌüó significant number of workers ŌüŻin the manufacturing sector could face unemployment.
Moreover, theŌüż strategic pivot adopted by manufacturers mayŌüó not only impact production locally but could also lead to an Ōüżexcess of goods in the chinese market, straining Ōüżeconomic equilibrium. ŌĆīInternational businesses are likely to scout newŌĆī locations ŌĆŹfor manufacturing to mitigate ŌĆīthe effects of tariffs,ŌĆī with countries in SoutheastŌüŻ Asia becoming more Ōüóappealing alternatives. This can be visualized ŌĆŹin Ōüżthe followingŌĆŹ table:
| country | Potential Advantages |
|---|---|
| Vietnam | Lower labor costs and favorable trade agreements |
| India | LargeŌüó workforce andŌüŻ growing market |
| Bangladesh | EstablishedŌüż textile manufacturing base |
theŌĆŹ direct consequences ofŌüż such Ōüża tariff increase extend beyond immediate economic impacts, Ōüżdriving a reevaluation of China’s manufacturing strategies and possibly leading to ŌĆīlong-term shifts in global manufacturingŌüŻ paradigms. The ongoing ŌĆīvolatility in trade relations necessitatesŌĆī a keen observationŌĆŗ of howŌĆŹ businesses adapt within ŌüŻthis challenging landscape.
Potential Responses from Chinese Government and ŌüżBusinesses
The imposition of aŌüó 54 percent tariff on ChineseŌĆŗ goods could prompt a multifacetedŌüŻ responseŌüó fromŌĆŹ both the Chinese government and its business sector. Government officials Ōüó may choose to retaliate with their own ŌĆŹtariffs aimed at U.S. products, leveraging ChinaŌĆÖs vast consumer market as a bargaining ŌĆŗchip. Additionally, they might mobilize state-owned enterprises to adjust their supply chains andŌüó operational strategies to mitigate the impact of these tariffs.ŌĆŹ Some ŌüópotentialŌüó actions might include:
- Accelerating domestic production to reduce dependency on U.S.ŌĆŹ imports.
- Enhancing bilateral tradeŌüŻ agreements with other countries to diversify ŌĆīexport ŌüŻmarkets.
- Implementing ŌĆŗsubsidiesŌüż for affected industries to support local businesses.
On the business front, Chinese ŌüŻcompanies will likelyŌüó reassess ŌüŻtheir ŌüópositioningŌĆī within global markets to ŌüŻadapt to changing economic conditions. Firms that rely ŌĆŗheavily on ŌüŻexports to the ŌüżU.S. may explore alternative markets inŌĆŗ Asia and Europe, while others could ŌĆīinnovate product lines to offer higher value, thus justifying costs under increased tariffs. ThisŌüŻ could lead to strategic ŌĆīshifts, such as:
- Investing in R&D for lower-cost alternatives.
- Strengthening ŌĆŗsupply chains by sourcing materials domestically.
- Enhancing marketing strategies to capture domestic consumer interest.
| Response Type | Government Actions | Business Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| TariffŌĆŗ Retaliation | Impose tariffs on U.S. goods | Seek alternativeŌĆŹ markets |
| Domestic Production | Boost ŌĆŗlocal manufacturing | Invest in R&D |
| Diversification | Form Ōüżnew trade agreements | Enhance product lines |
In Summary
the Ōüżimposition ofŌĆī a 54 percent tariff on Chinese imports represents a significant escalation in U.S.-China trade tensions, reflecting a broader strategy byŌüó the Trump administration to reshape international trade dynamics. AsŌĆŹ businesses andŌüŻ consumersŌüż brace Ōüżfor the ripple effects of these tariffs, the potential for increased prices on imported goods and heightened market volatility looms ŌĆŹlarge. Analysts Ōüżsuggest that such measures could provoke retaliatory actions from China, further complicating an Ōüżalready fraught economic relationship. As stakeholders navigate this complex landscape, the long-term implications ofŌüż these tariffs on the global economy remainŌüó to ŌüŻbe Ōüżseen, ŌüŻunderscoring the critical interplay between trade policy and geopolitical stability in a ŌüżrapidlyŌüż changing world. As the situation develops, close attention will be ŌĆŗrequired to ŌĆīunderstand ŌüżtheŌĆŹ ramifications for international trade and economic cooperation.