Japan’s Mounting Debt Crisis: Navigating Fiscal Challenges Amid Economic Uncertainty
Japan’s Debt Surpasses Twice Its GDP, Raising Alarms Over Economic Stability
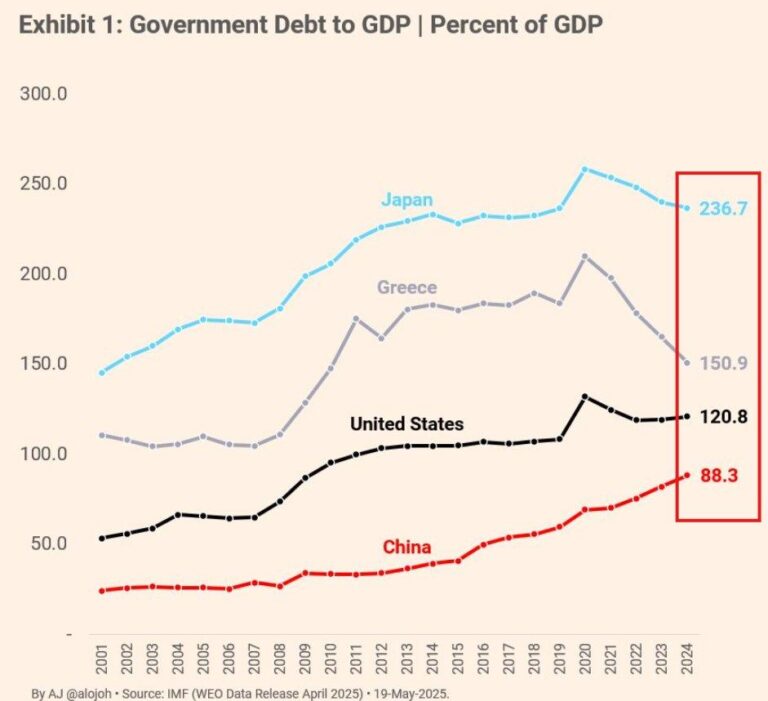
Japan is confronting an extraordinary fiscal challenge as its national debt has ballooned to over 230% of its gross domestic product (GDP), a figure that dwarfs most developed economies. This surge results from prolonged economic stimulus efforts, demographic shifts marked by an aging population, and escalating social welfare expenditures. The government now faces the daunting task of balancing initiatives aimed at stimulating growth with the imperative to restore fiscal discipline.
The enormity of Japan’s debt load has sparked intense discussions among economists and policymakers about potential strategies to safeguard long-term economic health. Key proposals include:
- Overhauling pension and healthcare frameworks to manage rising costs effectively
- Incrementally raising consumption taxes as a means to increase public revenues without stifling demand abruptly
- Fostering innovation-driven growth, leveraging technology and productivity enhancements for sustainable expansion
| Fiscal Indicator (2024) | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Public Debt-to-GDP Ratio | 230% |
| Total Government Expenditure (% of GDP) | 40% |
| Expected Increase in Tax Revenues from Reforms | Approximately 1.5% |
This unprecedented debt level places Japan in a unique position globally, where maintaining investor confidence while implementing necessary reforms remains critical.
The Urgency for Structural Reforms Amid Rising Fiscal Pressures
The escalation of Japan’s public debt-now exceeding an alarming threshold near 260% of GDP according to recent estimates-has intensified calls for decisive policy action. Without meaningful reform, experts warn that the country risks jeopardizing its fiscal sustainability and economic resilience.
A consensus is emerging around targeted austerity measures combined with tax restructuring designed not only to reduce deficits but also preserve social equity amid demographic challenges:
- Curtailing pension payouts progressively aligned with fiscal realities and life expectancy trends;
- Simplifying healthcare subsidies while incentivizing cost-efficiency within medical services;
- A phased approach toward increasing consumption taxes paired with compensatory relief programs for vulnerable populations.
- Diversifying revenue sources by introducing progressive taxation systems rather than relying heavily on regressive consumption taxes;
- Tightening government expenditure through eliminating inefficiencies and redundancies across departments;
| Policy Initiative | Estimated Savings (Trillions JPY) | Projected Implementation Period | < / tr >
|---|---|---|
The government must carefully balance these reforms against potential social backlash while ensuring long-term budgetary health.
Pursuing Sustainable Growth Through Comprehensive Policy Overhaul
The scale of Japan’s liabilities demands transformative changes beyond incremental adjustments. Leading economists advocate for broad structural reforms aimed at revitalizing economic dynamism alongside prudent fiscal management:
| Policy Domain | Current Challenge | Recommended Action /tr> /thead> |
|---|---|---|
|
/tbody> /table> This multi-pronged strategy aims not only at stabilizing finances but also positioning Japan competitively in a rapidly evolving global economy increasingly shaped by technological innovation and demographic shifts. Navigating Forward: The Stakes for Japan’s Economic Future Are HighThe reality that Japan’s national debt exceeds twice its annual output presents one of the most formidable challenges faced by any advanced economy today. Policymakers are tasked with steering between preserving essential social programs vital to millions while instituting tough reforms necessary for financial viability. The decisions made over the next few years will have profound implications-not just domestically but internationally-as investors watch closely how Tokyo manages this delicate balancing act amid global uncertainties such as shifting trade dynamics and geopolitical tensions. If successful, these efforts could serve as a blueprint for other nations grappling with similar demographic pressures coupled with high sovereign indebtedness; failure could risk prolonged stagnation or financial instability impacting markets worldwide. |