On June 15, 2025, escalating tensions in the South China Sea intersected with groundbreaking advances in 3D printing technology, capturing global attention. CBS News reports on how this strategic maritime hotspot faces increasing geopolitical risks amid rapid technological developments that could reshape defense and manufacturing capabilities in the region. This article examines the latest developments, exploring the implications for international security and technological innovation.
Rising Tensions in the South China Sea and Their Global Implications
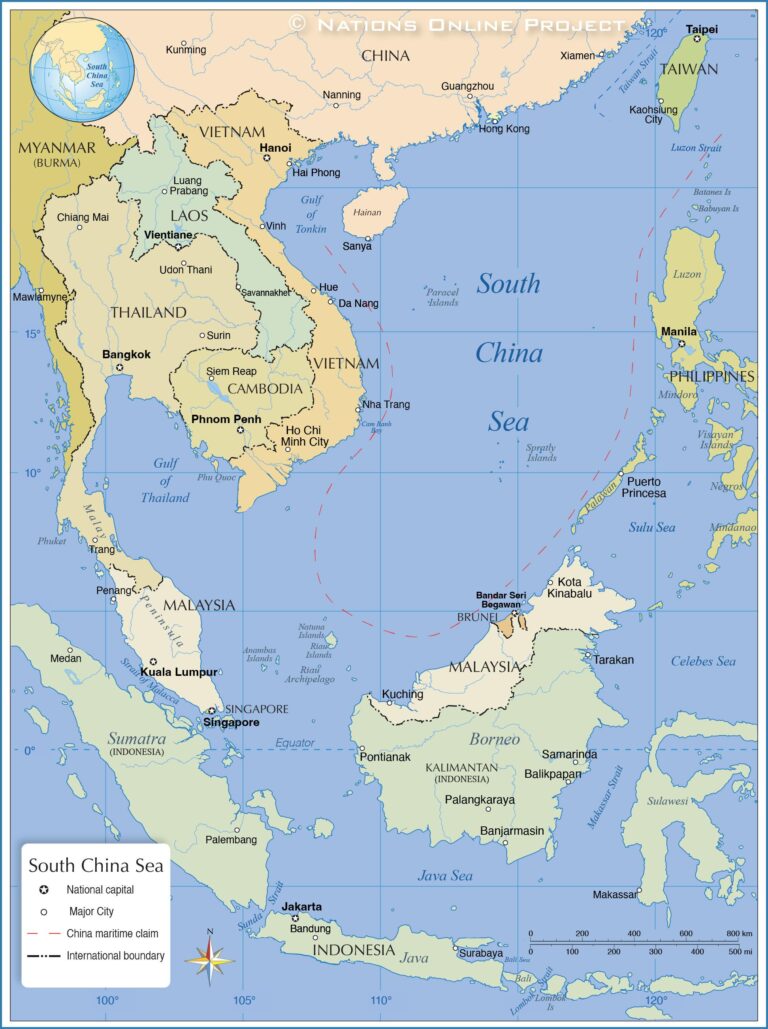
The South China Sea remains a volatile flashpoint where competing territorial claims have intensified naval presence and diplomatic friction among claimant nations. Recent satellite imagery confirms a surge in military installations on several man-made islands, escalating regional mistrust. Analysts warn that this militarization disrupts vital international shipping lanes, threatening global trade flows estimated to handle over 40% of maritime cargo passing through these waters. As regional powers increase joint military exercises and establish new defense outposts, the risk of accidental confrontations grows, signaling possible broader geopolitical consequences.
Economic and strategic interests intertwine as countries beyond the region express growing concern. The United States, Japan, and Australia have reaffirmed commitments to freedom of navigation operations, drawing sharp rebukes from Beijing, which considers these maneuvers as infringements on sovereignty. Below is a summary of recent military activities reported in the South China Sea, showcasing the scale and diversity of deployments:
| Country | Type of Deployment | Reported Increase % (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| China | Artificial island fortifications & missile systems | 35% |
| Philippines | Coast guard patrols & naval escorts | 20% |
| Vietnam | Maritime surveillance drones | 25% |
| United States | Freedom of navigation naval exercises | 30% |
- Strategic competition could trigger larger confrontations involving global powers.
- Global supply chains face disruptions with heightened military activity.
- Diplomatic efforts continue but with limited success amid entrenched positions.
Innovations in 3D Printing Technology Driving Economic and Security Shifts
Breakthroughs in 3D printing have accelerated the pace at which nations innovate, reshaping both economies and military capabilities globally. The technology now enables rapid prototyping and localized production of vital components, reducing dependence on traditional supply chains. This shift poses new challenges in regions like the South China Sea, where territorial disputes intersect with emerging tech advantages. Governments are investing heavily in additive manufacturing to gain strategic leverage, ensuring faster replenishment of critical maritime hardware, unmanned systems, and specialized equipment.
Among the most impactful innovations are:
- High-strength composite materials that withstand harsh maritime environments
- On-demand printing of spare parts for naval and commercial vessels
- Miniaturized drones and surveillance devices produced at scale with enhanced capabilities
| Innovation | Economic Impact | Security Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-based printing materials | Lower production costs, eco-friendly supply chains | More resilient equipment, reduced logistics footprint |
| Multi-material printing | Versatile product design, expanded manufacturing scope | Ability to create complex defense components on demand |
| Distributed manufacturing hubs | Decentralized economic growth, increased industrial agility | Harder to target supply networks, faster equipment deployment |
Policy Recommendations for Navigating Geopolitical Risks and Embracing Technological Advances
To effectively mitigate the escalating geopolitical tensions in the South China Sea while harnessing the potential of emerging technologies like 3D printing, policymakers must prioritize adaptive strategies grounded in collaboration. Strengthening multilateral dialogues between regional stakeholders can reduce misunderstandings and promote transparency, fostering an environment where technological innovation is not weaponized but rather leveraged for sustainable development. Governments should encourage joint research initiatives that use 3D printing to enhance defense readiness and civilian infrastructure simultaneously, creating dual-use innovations that serve public and security interests.
Furthermore, comprehensive regulatory frameworks are essential to balance security concerns with technological progress. Key policy actions include:
- Establishing cybersecurity protocols for protecting 3D printing intellectual property and sensitive data
- Implementing export controls to prevent the proliferation of potentially destabilizing technologies
- Promoting public-private partnerships to accelerate the integration of 3D printed solutions in disaster relief and infrastructure repair
| Policy Focus | Objective | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Multilateral Cooperation | Reduce conflict escalation | Enhanced regional stability |
| Technology Regulation | Secure innovation ecosystem | Balanced progress and safety |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Drive efficient technology use | Resilience in crisis response |
Future Outlook
As tensions continue to simmer in the South China Sea, the developments highlighted on June 15, 2025, underscore the complexities of regional security and the evolving role of emerging technologies like 3D printing in modern conflicts. Staying informed on these critical issues remains essential as stakeholders navigate a precarious landscape marked by both geopolitical rivalry and rapid technological advancement. CBS News will continue to monitor the situation closely, providing updates as new information emerges.