Spain has attributed the widespread power outage that plunged large parts of the country into darkness last April to an “overvoltage” incident, officials confirmed. The unexpected surge in electrical voltage disrupted the national grid, leading to significant blackouts that affected millions of residents and caused widespread disruption. Authorities are now investigating the technical causes behind the event, while energy experts weigh in on the implications for Spain’s power infrastructure and future grid stability.
Spain Attributes April Power Outage to Overvoltage Incident Affecting Nationwide Grid
The nationwide blackout that disrupted millions of households and businesses across Spain in April has been traced back to an overvoltage event within the country’s electrical grid. Authorities revealed that this unexpected surge in electrical pressure caused critical infrastructure failures, prompting widespread outages that lasted several hours. This overvoltage incident not only impacted urban centers but also posed serious challenges to power distribution in rural areas, highlighting vulnerabilities in the national grid’s current configuration.
Key factors identified in the overvoltage event include:
- Malfunctioning voltage regulation systems within key substations
- Insufficient fail-safes to counteract sudden voltage spikes
- Delayed response times by grid operators in detecting anomalies
| Impact Area | Duration of Outage | Affected Population |
|---|---|---|
| Madrid | 4 hours | 3 million |
| Catalonia | 3.5 hours | 2.4 million |
| Andalusia | 5 hours | 2.8 million |
Energy experts urge the government to Implement comprehensive upgrades to the electrical grid infrastructure, including the installation of advanced voltage regulation technology and improved fail-safe mechanisms. They also recommend enhancing real-time monitoring systems to detect and respond to anomalies more swiftly. These measures are crucial to prevent future overvoltage events, secure critical services, and ensure consistent power supply across both urban and rural areas. Additionally, training programs for grid operators on emergency protocols and anomaly detection are advised to reduce response times and mitigate the impact of such incidents.
Experts Analyze Technical Causes Behind Overvoltage and Its Impact on Energy Stability
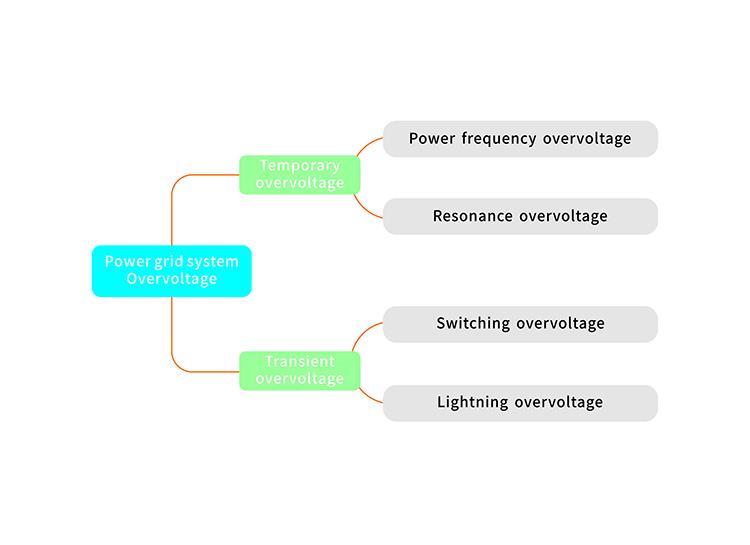
Specialists investigating the recent surge in Spain’s power grid point to overvoltage incidents as a critical trigger behind the widespread outages experienced in April. Overvoltage-an abnormal increase in the electrical potential beyond standard operating limits-can stem from various technical mishaps, including transformer failures, erroneous grid protection settings, or sudden disruptions in load balancing. Experts emphasize that such spikes strain interconnected infrastructure, leading to protective shutdowns designed to prevent equipment damage but, paradoxically, causing cascading power interruptions. The intricate nature of Europe’s interconnected energy landscape means that a fault in one segment can rapidly propagate, destabilizing broader regions.
The technical breakdown can be summarized by the following key factors contributing to overvoltage events:
- Improper grid synchronization: Failures in aligning phase angles among network nodes
- Faulty electrical insulation: Accelerated wear or damage facilitating current leaks
- Autotransformer malfunctions: Inadequate voltage regulation during demand surges
- Lack of real-time monitoring: Delayed response to voltage anomalies
These vulnerabilities collectively impair energy stability, threatening not only continuity of supply but also the long-term reliability of the system. The table below outlines a simplified impact matrix showcasing the relationship between overvoltage causes and system consequences:
| Technical Cause | Immediate Effect | Grid Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Transformer failure | Voltage spike | Protective shutdowns |
| Phase misalignment | Power oscillations | Frequency instability |
| Insulation breakdown | Short circuits | Equipment damage risk |
| Delayed monitoring | Uncontrolled voltage rise | Widespread power cuts |
Recommendations for Preventing Future Overvoltage Events in Spain’s Power Infrastructure
To significantly reduce the risk of future overvoltage incidents, Spanish energy authorities and grid operators must enhance real-time monitoring and control systems. Upgrading infrastructure with smart grid technologies – capable of instantaneously detecting voltage fluctuations – will improve responsiveness and prevent faults from escalating into large-scale outages. Additionally, integrating advanced sensor networks across key transmission nodes will enable predictive maintenance, minimizing unexpected overvoltage triggers caused by equipment degradation or environmental factors.
Implementation of robust coordination protocols among regional operators is also essential. A reinforced communication framework can facilitate rapid load balancing and dynamic voltage regulation during demand surges or supply interruptions. Key preventive measures include:
- Deployment of cutting-edge surge arresters and voltage suppressors
- Regular stress testing of grid components under simulated fault conditions
- Investment in energy storage systems to absorb sudden voltage spikes
- Comprehensive staff training on emergency voltage control procedures
| Preventive Measure | Expected Impact | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Grid Sensors | Early fault detection | 1-2 years |
| Surge Arresters | Voltage spike suppression | 6-12 months |
| Energy Storage Systems | Load stabilization | 2-3 years |
Future Outlook
The April power outage that disrupted electricity across parts of Spain has been officially attributed to an overvoltage incident, authorities confirmed. While the root causes continue to be investigated, the episode has underscored the vulnerabilities in the region’s power infrastructure and the urgent need for enhanced grid resilience. As Spain works to prevent future disruptions, the incident serves as a reminder of the critical importance of electrical system stability in maintaining daily life and economic activity.