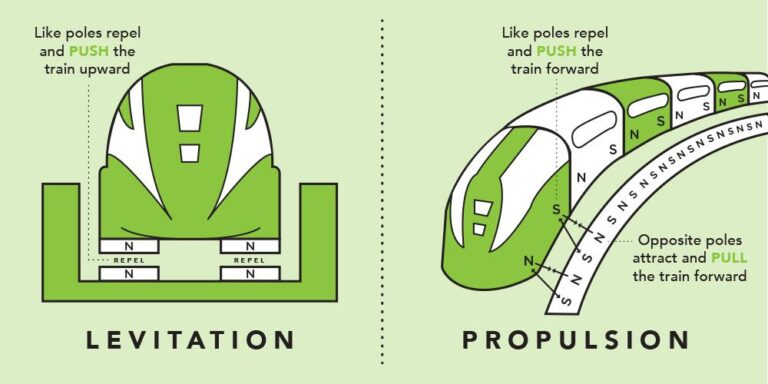
China is intensifying its efforts to close the gap with Japan in high-speed magnetic levitation (maglev) train technology, marking a significant push in Asia’s race for transportation supremacy. As Tokyo boasts one of the world’s fastest operational maglev services, Beijing is accelerating development and testing of its own advanced maglev systems, aiming to boost travel speeds and reshape regional connectivity. This move underscores China’s broader ambitions to lead in cutting-edge infrastructure and redefine high-speed rail standards across the continent.
China’s Maglev Ambitions Intensify Amid Regional Transportation Race
China’s commitment to expanding its maglev network has taken a decisive leap, signaling a strategic push to rival Japan’s long-established magnetic levitation technology. With plans to unveil new routes capable of reaching speeds beyond 600 kilometers per hour, Chinese engineers are focusing on innovation that blends cutting-edge propulsion systems with sustainable energy solutions. The acceleration in development underscores a broader ambition to enhance regional connectivity, reducing travel times dramatically between urban hubs like Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou, while also boosting economic integration across neighboring provinces.
Key factors fueling this maglev race include:
- Government support: Increased funding and policy incentives aimed at high-speed rail advancements.
- Technological breakthroughs: Advances in superconducting materials and track stability techniques.
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborative ventures with local manufacturers and global technology firms.
This concerted effort is designed to balance speed with affordability, making maglev travel a feasible option for millions of passengers in the coming decade. Below is a snapshot comparison of the maglev projects underway in China and Japan:
| Aspect | China | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Speed | Up to 620 km/h | Mid-600s km/h |
| Operational Lines | 3 (expanding) | 1 major commercial |
| Projected Expansion | Multiple new links by 2030 | Incremental upgrades |
| Environmental Focus | Renewable energy integration | Energy efficiency improvements |
Technological Advancements and Infrastructure Challenges in China’s High-Speed Rail Expansion
China’s push to dominate high-speed rail technology has faced substantial technical hurdles as engineers strive to develop maglev trains capable of competing with Japan’s renowned systems. Key challenges include achieving higher operational speeds without compromising safety, integrating advanced magnetic levitation technology with existing rail infrastructure, and enhancing energy efficiency to meet environmental goals. Innovations such as superconducting magnets and AI-driven predictive maintenance are being tested extensively to overcome these barriers. However, balancing cutting-edge technology deployment with mass-market scalability remains a delicate equation for Chinese rail planners.
Infrastructure limitations further complicate expansion efforts. While China boasts the world’s largest high-speed network, certain regions still lack the robust foundational support needed for ultra-high-speed maglev lines. Issues such as land acquisition delays, geological unpredictability, and the cost of upgrading legacy rail corridors have slowed progress. Below is a summary of critical infrastructure challenges impacting various provinces:
| Province | Main Issue | Projected Delay (months) |
|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | Subsurface soil instability | 6 |
| Guangdong | Urban land acquisition | 8 |
| Hubei | Legacy infrastructure retrofitting | 5 |
Key technological responses include:
- Deploying modular rail segments for rapid installation
- Advanced materials to withstand extreme speeds and environmental pressures
- AI-enhanced real-time monitoring systems to ensure operational safety
Strategic Policy Recommendations to Strengthen China’s Maglev Competitiveness Against Japan
To outpace Japan in the high-speed maglev arena, China must embrace a multi-faceted approach centered on technological innovation and international collaboration. Prioritizing investment in next-generation superconducting magnets and reducing overall project costs could place China at the forefront of efficiency and affordability. Furthermore, fostering partnerships with global industry leaders and academic institutions will accelerate R&D, ensuring breakthroughs in speed, safety, and energy consumption. Equally critical is the creation of robust intellectual property frameworks that protect Chinese innovations while enabling seamless knowledge exchange across borders.
Key initiatives to consider include:
- Scaling advanced maglev manufacturing capabilities through automated production lines to reduce costs and improve consistency.
- Expanding maglev infrastructure projects strategically within and beyond domestic borders to strengthen market presence.
- Incentivizing private sector engagement via tax breaks and innovation grants targeting cutting-edge maglev technologies.
- Enhancing public acceptance and awareness by demonstrating economic and environmental benefits in pilot cities.
| Strategic Pillar | Focus Area | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Superconducting Magnets R&D | 50% increase in speed efficiency |
| Industry | Automated Manufacturing | Cost reduction by 30% |
| Policy | Innovation Incentives | Boost private sector participation |
| Market | International Expansion | Broaden global footprint |
Final Thoughts
As China pushes forward with advancements in maglev technology, its accelerated efforts signal a determination to challenge Japan’s longstanding leadership in high-speed rail innovation. While Tokyo has set a high standard with decades of operational expertise, Beijing’s ambitious projects underscore the shifting dynamics in Asia’s transportation landscape. The race to develop faster, more efficient maglev trains not only reflects national pride but also a strategic drive to harness cutting-edge infrastructure for economic growth. As both countries navigate this competitive trajectory, the coming years will reveal which vision ultimately defines the future of ultra-high-speed rail in the region.