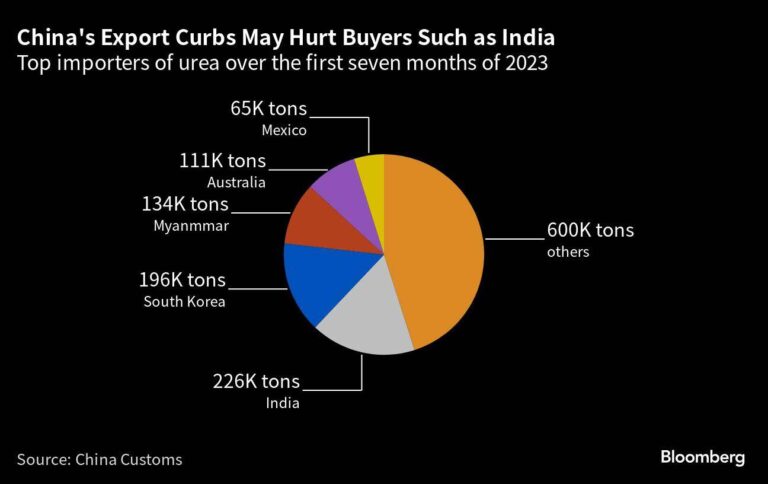
In a significant development signaling a potential easing of recently heightened tensions, China has announced a relaxation of restrictions on urea exports to India. This move, reported by Bloomberg, comes amid ongoing diplomatic efforts to stabilize the often fraught relationship between the two neighbors. Analysts view China’s decision as a strategic step to bolster agricultural supply chains in India while opening channels for improved bilateral trade and cooperation.
China Eases Urea Export Restrictions to India Signaling Improved Bilateral Relations
In a significant development that hints at warming ties between Beijing and New Delhi, Chinese authorities have eased urea export restrictions to India. The decision comes after a period of heightened trade friction and geopolitical tension, marking a potential shift towards cooperation in agricultural trade. Indian farmers, who rely heavily on urea as a key fertilizer input, stand to benefit from improved supply chains and potentially lower costs following this policy change.
The relaxation of export limits is expected to impact several sectors positively, emphasizing the growing interdependence between the two economies. Key points of this easing include:
- Increased export quotas: Allowing larger volumes of urea shipments to India on a monthly basis.
- Streamlined customs procedures: Faster clearance times aimed at reducing delivery delays.
- Price stabilization: Potential moderation in fertilizer prices benefiting end-users across agricultural regions.
| Aspect | Before Easing | After Easing |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Export Quota (tons) | 50,000 | 100,000 |
| Customs Clearance Time | 10-15 days | 4-7 days |
| Expected Impact on Price | Increasing | Stable to Decreasing |
Impact of Relaxed Export Controls on India’s Agricultural Sector and Fertilizer Supply Chain
China’s decision to ease export controls on urea supplies to India is poised to alleviate long-standing supply chain bottlenecks that have affected the Indian agricultural sector. For months, Indian farmers faced challenges due to limited access to affordable fertilizer, which in turn impacted crop yields and overall agricultural productivity. The relaxation signals a strategic shift that could stabilize input costs, boost timely availability of fertilizers, and enhance India’s food security outlook ahead of the critical planting season.
Key implications of this policy adjustment include:
- Reduced fertilizer shortages: By allowing increased urea imports, distribution networks can meet mounting domestic demands efficiently.
- Price stabilization: Greater supply inflows are expected to moderate fertilizer prices, easing financial pressure on farmers.
- Supply chain resilience: Improved cross-border cooperation can fortify logistics pathways and reduce dependency risks.
| Aspect | Before Export Relaxation | After Export Relaxation |
|---|---|---|
| Urea Availability | Limited and erratic | Steady and increased |
| Price Fluctuation | Highly volatile | More stable |
| Farmer Impact | Crop stress and reduced yields | Improved cultivation confidence |
| Trade Relations | Strained | Gradually improving |
Strategies for Indian Farmers and Policymakers to Optimize Benefits Amid Changing Trade Dynamics
In light of China’s decision to ease restrictions on urea exports to India, Indian farmers and policymakers must pivot their strategies to harness this opportunity effectively. For farmers, optimizing fertilizer use in tandem with improved supply can lead to enhanced crop yields and reduced production costs. Emphasis should be laid on adopting precision agriculture techniques and employing balanced fertilization to ensure sustainability and prevent nutrient runoff. Additionally, local agricultural bodies can facilitate training programs to educate farmers about the integration of imported urea with indigenous organic alternatives.
Policymakers, meanwhile, should channel efforts toward stabilizing fertilizer prices and ensuring equitable distribution across regions. By fostering transparency in the supply chain and monitoring import volumes, they can mitigate market volatility. Collaborative frameworks with China and other suppliers need to be strengthened to secure long-term contracts safeguarding against sudden trade disruptions. The following table summarizes key action points for stakeholders:
| Stakeholder | Key Actions | Expected Outcome | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmers |
|
Higher crop yield, cost-efficiency | ||||||||
| Policymakers |
|
In light of China’s decision to ease restrictions on urea exports to India, Indian farmers and policymakers must pivot their strategies to harness this opportunity effectively. For farmers, optimizing fertilizer use in tandem with improved supply can lead to enhanced crop yields and reduced production costs. Emphasis should be laid on adopting precision agriculture techniques and employing balanced fertilization to ensure sustainability and prevent nutrient runoff. Additionally, local agricultural bodies can facilitate training programs to educate farmers about the integration of imported urea with indigenous organic alternatives. Policymakers, meanwhile, should channel efforts toward stabilizing fertilizer prices and ensuring equitable distribution across regions. By fostering transparency in the supply chain and monitoring import volumes, they can mitigate market volatility. Collaborative frameworks with China and other suppliers need to be strengthened to secure long-term contracts safeguarding against sudden trade disruptions. The following table summarizes key action points for stakeholders:
|