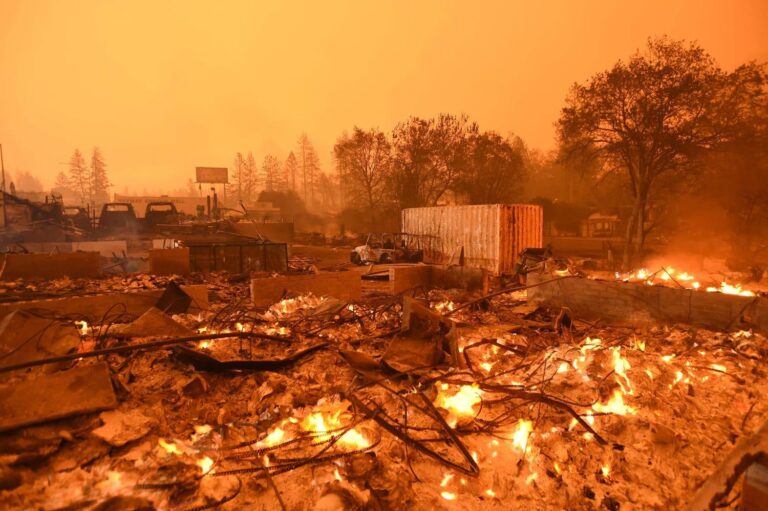
Spain is grappling with its most devastating wildfire season in nearly three decades, as recent blazes have scorched an alarming 382,607 hectares of land. According to official reports, this marks the worst wildfire damage since 1994, raising serious concerns about environmental impact and firefighting preparedness. The extensive destruction has prompted urgent responses from authorities and renewed calls for enhanced measures to combat increasingly frequent and intense wildfires across the country.
Spain Faces Unprecedented Wildfire Devastation Impacting Ecosystems and Communities
Spain is grappling with its most severe wildfire season since 1994, with 382,607 hectares of land scorched across multiple regions. The fires have not only ravaged vast forests but have also severely compromised local biodiversity, threatening endangered species and disrupting delicate ecosystem balances. Firefighters continue to battle the flames in some of the hardest-hit provinces, where prolonged drought and rising temperatures have exacerbated conditions. Rural communities that depend on agriculture and forestry face devastating economic losses and displacement, while emergency services remain stretched thin.
Authorities have reported widespread damage including:
- Wildlife habitats destroyed: accelerating the decline of native species
- Loss of arable land: jeopardizing food production in affected areas
- Air quality deterioration: creating health hazards for residents
- Infrastructure damage: roads and power lines disrupted, complicating recovery efforts
| Region | Hectares Burned | Containment Status |
|---|---|---|
| Andalusia | 120,453 | 50% Contained |
| Catalonia | 85,673 | 60% Contained |
| Valencia | 65,980 | 40% Contained |
| Galicia | 78,501 | 55% Contained |
Analyzing Root Causes and the Role of Climate Change in Escalating Fire Risks
The unprecedented scale of wildfires sweeping across Spain this year can be attributed to a complex interplay of environmental, human, and climatic factors. Prolonged drought conditions, paired with soaring summer temperatures, have created a tinderbox scenario throughout large swathes of the country. Neglected forest management practices, such as insufficient clearing of underbrush and accumulation of dry biomass, have further exacerbated the susceptibility of these landscapes to ignition and rapid fire spread. Meanwhile, increased human activity in rural areas-ranging from agricultural burns to accidental ignitions-remains a significant contributor to the onset of many of these blazes.
Climate change acts as a critical multiplier in escalating fire risks, intensifying the severity and duration of wildfire seasons. Rising average temperatures and altered precipitation patterns lead to extended dry spells and reduced soil moisture, effectively lengthening fire-prone periods. Below is a snapshot of climate factors influencing wildfire incidence in Spain (2023 data):
| Climate Factor | 2023 Value | Historical Average | Impact on Fires |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Summer Temperature (°C) | 33.5 | 29.7 | Increased heat stress on vegetation |
| Annual Rainfall (mm) | 350 | 450 | Lower moisture content in fuels |
| Days Without Rain | 65 | 50 | Prolonged dry conditions |
This data reveals a clear trend towards conditions that encourage larger and more intense fires, underscoring the growing importance of integrating climate adaptation strategies into fire prevention and response frameworks.
Experts Urge Strengthened Prevention Measures and Enhanced Emergency Response Strategies
Experts and environmental authorities are calling for a comprehensive overhaul of current wildfire prevention frameworks to mitigate the escalating risks posed by climate change and increasing human activity. Enhanced surveillance systems, including satellite monitoring and drone deployment, are recommended to detect early signs of fire outbreaks. Additionally, the implementation of community education programs focusing on fire safety and responsible land management is highlighted as a critical step toward reducing ignition sources across vulnerable regions.
To bolster emergency response efficacy, specialists advocate for increased investment in rapid deployment resources and improved inter-agency coordination at both local and national levels. The following table summarizes key proposed measures and their expected impact on wildfire management:
| Measure | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Advanced Fire Detection Technology | Faster identification and containment |
| Community Engagement Campaigns | Lower ignition rates through awareness |
| Inter-Agency Coordination Protocols | Streamlined emergency responses |
| Increased Funding for Firefighting Resources | Enhanced operational capacity |
In Summary
As Spain grapples with its worst wildfire season in nearly three decades, the scale of devastation underscores the urgent need for enhanced prevention and response strategies. With 382,607 hectares scorched, authorities face the daunting task of recovery amid concerns over climate change and increasing fire risks. The coming months will be critical in assessing the long-term environmental and economic impacts, as the nation seeks to rebuild and bolster resilience against future disasters.