Australia’s rental market has long been a subject of intense debate, with many narratives portraying it as increasingly unaffordable for everyday Australians. However, a recent analysis by SBS Australia challenges this prevailing perception, revealing a significant disconnect between the popular “rental affordability crisis” narrative and the actual conditions faced by renters across the country. This article delves into the findings that question widely held assumptions, unpacking the factors contributing to what some experts are now calling Australia’s rental affordability “myth.”
Australia’s Rental Affordability Crisis Revealed Through New Data
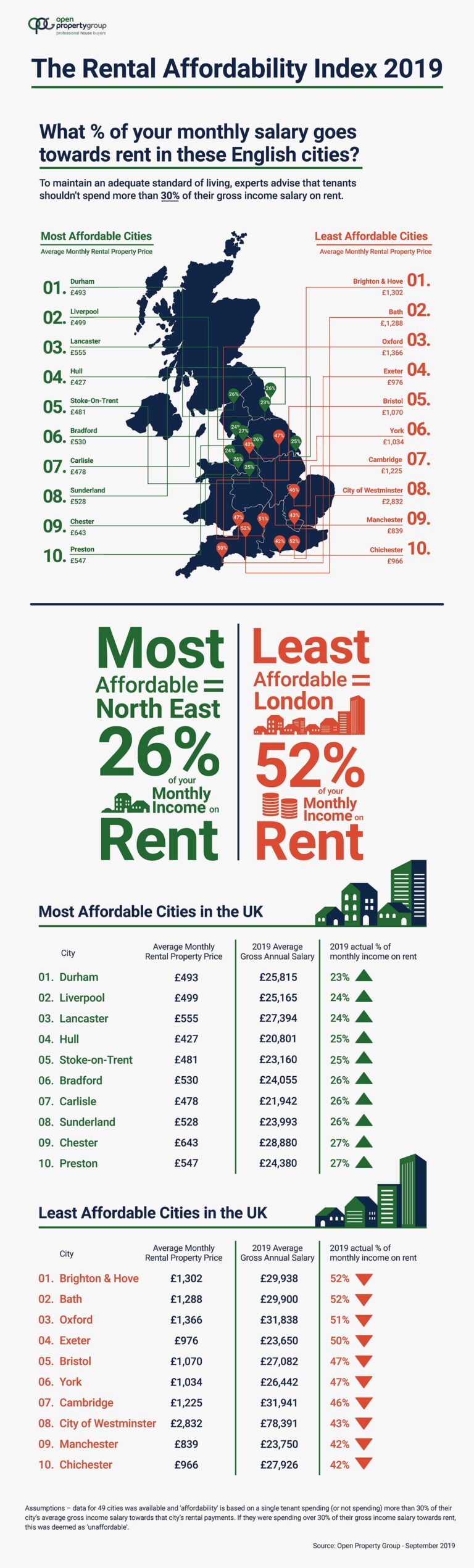
New comprehensive data has unveiled a harsh reality for many Australians struggling with rising rental costs, sharply contradicting the commonly held belief that rental affordability has remained stable. Despite claims from some quarters suggesting that the market has adjusted, recent figures show a consistent increase in median rents across major cities, disproportionately affecting low-to-middle income households. This shift has amplified financial stress, contributing to a growing divide between income levels and accessible housing options.
Key factors highlighted by the data include:
- Average rental prices rising by over 15% in the past two years, outpacing wage growth.
- Less than 30% of rental properties now considered affordable for households earning minimum wage.
- Regional imbalances, with some rural areas experiencing sharper increases due to migration shifts.
| City | Median Rent Increase (2 Years) | Affordability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney | +18% | 25% |
| Melbourne | +16% | 28% |
| Brisbane | +14% | 31% |
| Adelaide | +12% | 34% |
Government Policies and Their Impact on Housing Costs for Renters
Government interventions have long been touted as solutions to ease rental pressures, but their effectiveness in curbing housing costs for tenants remains contentious. Rent control policies, often implemented to protect renters from steep price hikes, can sometimes have the paradoxical effect of reducing the overall housing supply, as landlords become reluctant to invest in maintenance or new developments. Similarly, subsidies and support schemes targeting low-income renters have finite reach and are frequently overwhelmed by demand, leading to uneven distribution and limited impact on the broader rental market.
Taxation and zoning reforms also play pivotal roles in shaping affordability, yet they often produce mixed outcomes. For instance, incentives for developers to build affordable dwellings can be offset by challenges such as local opposition and rising construction costs. Below is a simplified overview of key policy tools and their observed impacts on rental markets:
| Policy Measure | Intended Impact | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Rent Control | Limit rent increases | Reduced new rental property supply |
| Housing Subsidies | Support low-income renters | Insufficient coverage, high demand |
| Tax Incentives for Developers | Increase affordable housing stock | Variable uptake, local opposition |
| Zoning Reforms | Encourage higher-density builds | Slower implementation, mixed effects |
- Short-term policies may ease immediate pressures but often fail to address systemic issues.
- Long-term strategies require coordinated efforts across multiple government levels and sectors.
- Transparent data and ongoing monitoring are essential for policy refinement and achieving meaningful affordability.
Strategies for Improving Rental Affordability and Protecting Vulnerable Tenants
Addressing rental affordability requires a multi-faceted approach centered on policy reform and tenant protections. Governments must consider increasing the supply of affordable housing through targeted investment in social and community housing projects. Additionally, rent control measures that limit excessive increases can offer immediate relief to tenants facing financial strain. Equally important is the introduction of stronger legal frameworks to safeguard vulnerable renters, ensuring they are shielded from arbitrary evictions and unfair lease conditions.
Community engagement and support networks also play a critical role in stabilizing the rental market. Some effective strategies include:
- Implementing rental assistance programs that cater to low-income households and reduce the risk of homelessness.
- Enhancing tenant education to empower renters with knowledge about their rights and responsibilities.
- Encouraging partnerships between local councils and non-profit organizations to develop tailored rental solutions.
| Strategy | Immediate Impact | Long-term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rent Control Legislation | Rent Stabilization | Market Balance |
| Social Housing Expansion | Increased Availability | Reduced Homelessness |
| Tenant Rights Education | Informed Renters | Stronger Advocacy |
The Way Forward
As Australia’s rental market continues to tighten, the narrative of affordability presented by some official reports clashes starkly with the lived experiences of many renters. This investigation highlights the urgent need for more transparent data and policies that address the true cost and scarcity of rental housing. Without a clear understanding of the realities on the ground, efforts to improve housing affordability risk remaining out of reach for those most affected.