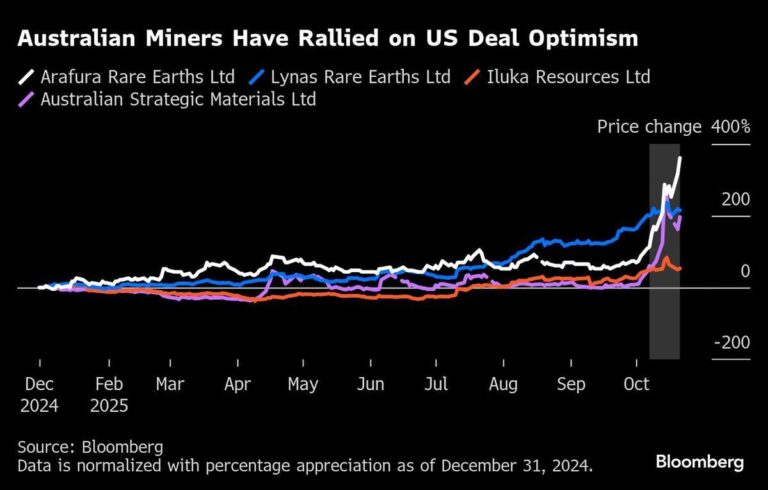
In a strategic move aimed at reshaping the global rare earths supply chain, the United States and Australia have forged a landmark agreement to bolster collaboration and reduce dependency on China’s dominant market position. Announced this week, the deal marks a significant step toward diversifying critical mineral sources essential for advanced technologies and national security. However, analysts caution that despite this initiative, China’s entrenched control over rare earth production and processing is unlikely to diminish rapidly, underscoring the complexities that lie ahead in efforts to balance geopolitical interests with economic realities.
US Australia Rare Earths Agreement Signals Strategic Shift in Global Supply Chains
The newly inked agreement between the United States and Australia highlights a deliberate move towards diversifying rare earth mineral supply chains, traditionally dominated by China. This bilateral deal focuses on developing sustainable mining and processing capabilities in Australia, coupled with critical investments in refining technology within the US. However, despite these strategic efforts, experts caution that the entrenched dominance of Chinese control over global rare earth markets-accounting for roughly 60% of refined output-remains a formidable challenge for restructuring supply dynamics in the near term.
Key aspects of the US-Australia partnership include:
- Joint R&D initiatives targeting green extraction processes
- Investment incentives to scale up domestic refining capacity
- Establishment of a rare earths stockpile to mitigate supply disruptions
- Collaboration on environmental and regulatory standards
| Country | Global Rare Earth Production Share | Refining Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 57% | 60% |
| Australia | 17% | 5% |
| United States | 5% | 10% |
| Others | 21% | 25% |
Challenges Remain as China Maintains Dominance in Rare Earths Production
Despite growing international efforts to diversify the rare earths supply chain, significant obstacles persist that reinforce China’s enduring dominance. The country’s unparalleled infrastructure, ranging from mining to refining capabilities, provides an economic moat that newcomers find difficult to breach. Additionally, environmental regulations and high capital investment requirements create barriers that slow down the scaling of alternative sources. Even with strategic partnerships like the recent US-Australia deal, these challenges underscore a landscape where China’s strategic advantages remain deeply entrenched.
Moreover, market dynamics driven by China’s production scale continue to influence global pricing and supply stability. Attempts to build resilient supply chains outside China still face hurdles such as:
- Long lead times: Bringing new mining projects online often takes several years.
- Technical complexity: Extracting and processing rare earth elements demand specialized expertise.
- Geopolitical risks: Diversification efforts can be hampered by international tensions and trade uncertainties.
| Key Factor | China’s Position | Challenges for Others |
|---|---|---|
| Mining Capacity | Over 60% global share | Limited new projects |
| Refining Technology | Advanced and cost-effective | High investment needs |
| Environmental Compliance | Relaxed enforcement | Stricter regulations |
Policy Recommendations for Strengthening US Australia Collaboration and Reducing Dependency
To truly transform the US-Australia rare earths partnership from a symbolic agreement into a strategic powerhouse, policymakers must focus on diversifying supply chains beyond traditional sources. This entails incentivizing domestic mining ventures within Australia with robust funding and streamlined regulatory pathways, while also investing in sustainable processing technologies that reduce environmental impact. Collaboration should extend to research and development initiatives aimed at unlocking alternative materials that can either complement or replace rare earth elements, thereby diminishing long-term reliance on China’s monopolistic hold.
Equally important is bolstering the resilience of critical supply networks through multilateral frameworks that involve other like-minded nations. Key recommendations include:
- Establishing a trilateral coordination body to pool intelligence, align standards, and synchronize export controls.
- Expanding joint investments in advanced mining and recycling infrastructure, creating economies of scale.
- Enhancing workforce training programs to nurture expertise in rare earth extraction and processing.
- Promoting market transparency to stabilize pricing and deter monopolistic behaviors.
| Policy Area | Proposed Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Supply chain diversification | Funding for domestic mines | Reduced Chinese dependency |
| Multilateral cooperation | Trilateral coordination body | Aligned regulations & controls |
| Technological innovation | Investment in R&D | Alternative materials development |
| Workforce development | Specialized training programs | Skilled labor pool expansion |
Insights and Conclusions
While the newly forged US-Australia rare earths agreement signals a strategic step toward diversifying supply chains and reducing dependence on China, experts caution that Beijing’s entrenched dominance in the sector will not be easily displaced. As both Washington and Canberra navigate the complex geopolitical and economic challenges ahead, the deal represents the beginning of a prolonged effort rather than an immediate game-changer. Monitoring developments in this critical industry will be essential, as the global balance of rare earths production and influence continues to evolve.