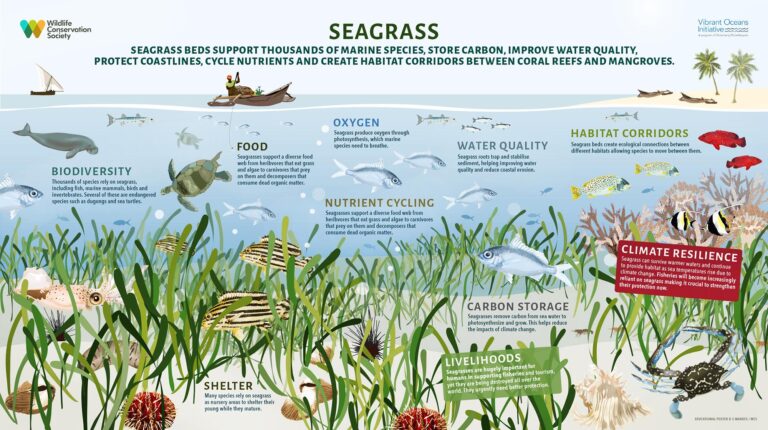
Scientists have completed the first comprehensive mapping of Italy’s entire coastline, unveiling a critical step forward in efforts to restore seagrass meadows and revitalize marine ecosystems. The extensive survey, detailed in a recent Mongabay report, provides unprecedented data on underwater habitats that serve as vital carbon sinks and biodiversity hotspots. This groundbreaking initiative is expected to inform targeted conservation strategies and bolster the resilience of Italy’s coastal waters amid mounting environmental pressures.
Scientists Complete Comprehensive Mapping of Italy’s Coastline to Boost Marine Conservation
A groundbreaking scientific effort has yielded the first-ever detailed map of Italy’s entire coastline, marking a significant advancement in marine conservation initiatives. Utilizing cutting-edge remote sensing technology combined with extensive in-situ surveys, researchers meticulously charted coastal habitats, with a special focus on vital seagrass meadows that serve as underwater carbon sinks and nurseries for diverse marine species. This comprehensive dataset is expected to inform targeted restoration projects, ensuring sustainable management of marine ecosystems threatened by climate change, pollution, and human encroachment.
The mapping project highlights several key habitat types along Italy’s shores, including:
- Posidonia oceanica meadows – the backbone of Mediterranean biodiversity
- Rocky reef systems hosting endemic species
- Sandy beaches and dunes crucial for coastal protection
- Artificial structures and their ecological impact
Early analysis reveals critical zones requiring immediate conservation efforts, providing policymakers and environmental groups with actionable data. Below is a concise overview of habitat distribution along the coastline:
| Habitat Type | Approximate Coverage (km²) | Conservation Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Posidonia meadows | 4,300 | High |
| Rocky reefs | 2,100 | Medium |
| Sandy beaches | 1,800 | High |
| Artificial structures | 750 | Low |
Detailed Seagrass Habitat Data Offers New Insights for Ecosystem Restoration Efforts
Utilizing advanced remote sensing technologies combined with in-situ observations, researchers have produced the most comprehensive seagrass distribution maps along Italy’s coastline to date. This unprecedented dataset provides critical insights into the health and extent of these vital underwater meadows, which serve as biodiversity hotspots, carbon sinks, and natural coastal protectors. The detailed information reveals previously unknown areas of degradation caused by pollution, coastal development, and climate-related stressors, enabling targeted restoration initiatives where recovery potential is highest.
Key findings highlight significant variation in seagrass density and species composition across different regions, influencing local marine ecosystem dynamics. Restoration projects can now leverage these insights to prioritize efforts and optimize resource allocation. For instance, areas identified with robust seagrass beds exhibit:
- Higher fish nursery productivity
- Improved water quality metrics
- Greater resilience to erosion and storms
To assist stakeholders, the study presents a summary of habitat conditions by region:
| Region | Seagrass Coverage (%) | Restoration Priority | Dominant Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liguria | 32 | High | Posidonia oceanica |
| Tuscany | 45 | Medium | Cymodocea nodosa |
| Apulia | 28 | High | Posidonia oceanica |
| Sicily | 40 | Medium | Cymodocea nodosa |
Experts Urge Policy Integration of Mapping Findings to Enhance Coastal and Marine Recovery Programs
Leading marine scientists emphasize that the groundbreaking coastal mapping of Italy provides a crucial foundation for enhancing conservation and rehabilitation strategies across Mediterranean waters. By integrating the comprehensive spatial data with existing recovery programs, policymakers can prioritize areas where seagrass meadows and other vital marine ecosystems are most vulnerable or fragmented. Experts advocate for adopting a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Targeted restoration efforts based on high-resolution habitat maps
- Adaptive management to respond dynamically to environmental changes and human pressures
- Collaborative governance involving local communities, scientists, and industry stakeholders
Furthermore, specialists highlight the importance of a standardized reporting framework to consistently track progress and setbacks in ecosystem recovery. Such an approach ensures transparent data sharing and fosters accountability among the various agencies involved. The following table summarizes the key benefits expected from policy integration of mapping data:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Informed Habitat Protection | Better preservation of critical marine areas |
| Efficient Resource Allocation | Optimized investment in restoration projects |
| Improved Monitoring | Early detection of ecosystem degradation |
| Community Engagement | Strengthened local stewardship and awareness |
In Conclusion
The comprehensive coastal mapping of Italy marks a significant step forward in marine conservation efforts, providing invaluable data to support the restoration of seagrass habitats and the broader health of marine ecosystems. As scientists continue to monitor these vital underwater landscapes, the insights gained will not only aid Italy’s environmental policies but also serve as a model for coastal conservation worldwide. This initiative underscores the critical role of cutting-edge research in safeguarding marine biodiversity amid growing ecological challenges.