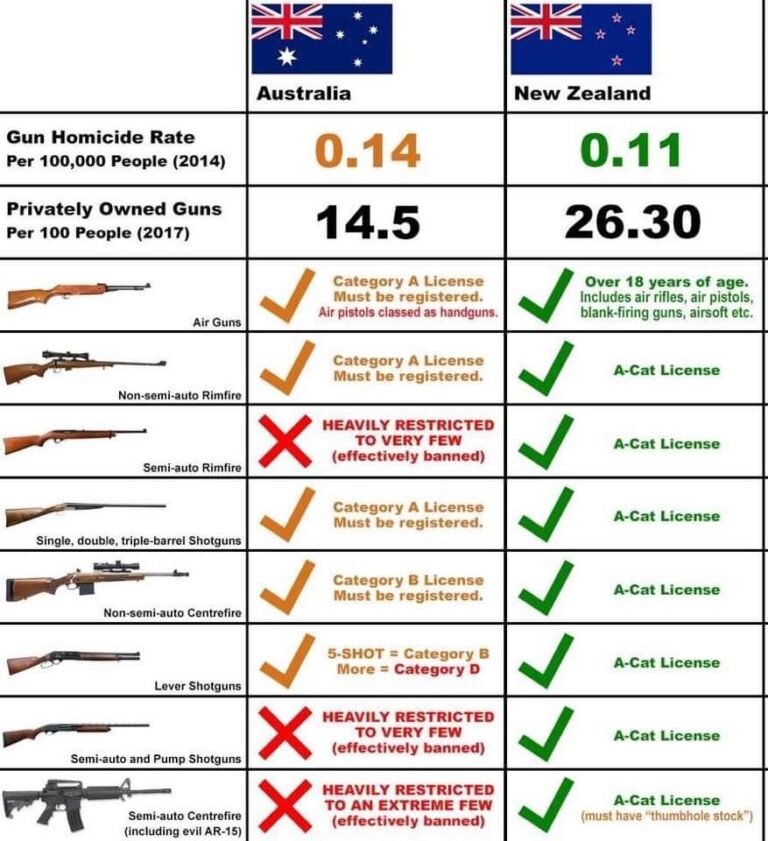
In recent years, Australia has witnessed a notable uptick in gun ownership, a development that has sparked debate across the nation. Once hailed for its stringent firearm regulations and low rates of gun-related violence, the country now faces questions about the factors driving this unexpected rise. From shifting public perceptions and legislative changes to evolving security concerns, this article explores the complex dynamics behind the surge in Australian gun ownership and what it could mean for the future.
Changing Social Attitudes and Economic Factors Driving Increased Firearm Purchases
Recent shifts in public perception have played a significant role in reshaping attitudes toward firearms in Australia. Growing concerns about personal security amid rising urban crime rates, coupled with the pervasive influence of social media, have fostered a renewed interest in gun ownership. This evolving mindset challenges the long-standing emphasis on strict gun control, with many now viewing firearms as essential tools for self-defense and protection of property. Furthermore, political discourse around individual rights and government trust has fueled a sense of urgency for some Australians to acquire firearms.
Economic conditions have also contributed to this trend. Inflationary pressures and a volatile job market have led individuals to consider firearms not just as defensive measures but also as potential assets. The rise in recreational activities like sport shooting and hunting is another driver, supported by increased disposable incomes in certain demographics. Below is a brief overview of key economic and social factors influencing the surge in firearm purchases:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Urban Crime Rates | Heightened concerns prompt increased self-defense purchases |
| Social Media Influence | Amplifies awareness and normalizes gun ownership |
| Economic Uncertainty | Leads to higher demand for firearms as tangible assets |
| Recreational Interests | Growth in sport shooting and hunting activities |
| Political Climate | Emphasis on personal freedoms encourages acquisition |
The Impact of Policy Shifts and Regional Variations on Gun Ownership Trends
Australia’s shifting landscape of gun ownership is deeply intertwined with evolving policy frameworks and distinct regional attitudes toward firearms. While national reforms like the 1996 gun buyback program initially curbed firearm prevalence, recent years have witnessed a nuanced resurgence in ownership driven by localized legislative relaxations and varying enforcement practices. States such as Queensland and Western Australia have introduced amendments that ease restrictions on certain categories of firearms, reflecting regional priorities around rural property protection and recreational shooting. These policy divergences underscore how legal frameworks and community needs shape access, resulting in a patchwork of ownership trends rather than a uniform national pattern.
Compounding these regulatory differences are socio-economic and cultural factors that vary across Australia’s vast geography. Rural communities often report higher gun ownership rates, citing practical necessities like pest control and farming activities. In contrast, urban centers maintain stricter controls, influenced by heightened concerns over crime and public safety. The table below encapsulates key state-level variations in gun laws and ownership estimates, highlighting the complexity behind the seemingly straightforward statistic of rising firearms possession.
| State | Recent Policy Changes | Estimated Gun Ownership (%) | Primary Ownership Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Queensland | Relaxed licensing for semi-automatic rifles | 22% | Rural property and farming needs |
| New South Wales | Strict enforcement, no major changes | 18% | Hunting and sports shooting |
| Victoria | Introduced tighter storage rules | 15% | Recreational shooting and security |
| Western Australia | Expanded permits for some firearm categories | 20% | Remote property protection |
- Policy shifts tend to reflect regional socioeconomic contexts, making a one-size-fits-all approach ineffective.
- Ownership trends are significantly influenced by the balance between urban regulatory pressure and rural practical demands.
- Understanding the nuances behind these variations is critical for informed debate on firearm regulation nationally.
Strategies for Addressing Safety Concerns Amid Rising Firearm Access
As firearm access expands, balancing individual rights with public safety becomes a pressing challenge. Implementing comprehensive background checks remains a cornerstone strategy, ensuring that sales and transfers include thorough vetting to prevent firearms from reaching individuals with criminal records or mental health concerns. Additionally, investing in community education programs can empower gun owners with responsible handling practices, reducing accidental injuries and misuse. These initiatives often involve collaboration between local authorities, health professionals, and firearm advocacy groups to create trust and reinforce safety without alienating responsible owners.
Policy makers are also exploring technological innovations such as smart guns equipped with biometric locks, which limit use to authorized individuals. Coupling these advancements with regular safety audits and secure storage requirements can mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access, especially in homes with children. The table below outlines key proposed measures and their potential impact on safety outcomes:
| Strategy | Implementation Focus | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Background Checks | Mandatory across all sales | Reduce illegal access |
| Smart Gun Technology | Biometric authorization | Lower accidental shootings |
| Secure Storage Laws | Firearm locks and safes | Prevent theft and misuse |
| Community Outreach | Education & awareness | Promote responsible ownership |
In Conclusion
As Australia continues to grapple with the complexities surrounding gun ownership, the recent rise signals a shift in public sentiment that demands close attention. Understanding the factors driving this increase-from changing perceptions of safety to evolving legislative landscapes-is essential for policymakers and communities alike. As the debate unfolds, ongoing analysis will be critical in shaping approaches that balance individual rights with collective security in Australia’s unique context.