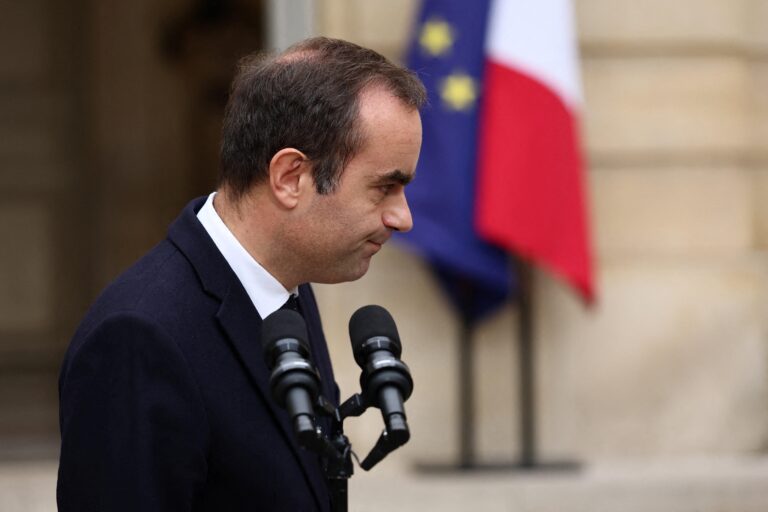
France’s political landscape has been jolted once again as Prime Minister Élisabeth Borne tendered her resignation, marking yet another upheaval in the country’s executive leadership. The announcement has immediately ignited calls from far-right parties demanding new national elections, intensifying the already volatile atmosphere ahead of the upcoming legislative session. This latest development underscores mounting tensions within France’s government and raises questions about the stability of President Emmanuel Macron’s administration as it navigates a deeply divided electorate.
France’s Prime Minister Steps Down for the Second Time in Political Turmoil
Amid growing political unrest, France’s Prime Minister has announced his resignation, marking the second time in recent months that the government faces a leadership shake-up. This unexpected move comes as the administration grapples with deepening internal divisions and mounting public dissatisfaction over economic policies and social reforms. The resignation has accelerated calls from far-right factions demanding a swift national election, arguing that the current government no longer represents the will of the people.
Key factors fueling the political crisis include:
- Widespread protests over pension reforms and wage stagnation
- Rising inflation and cost-of-living concerns
- Increasingly polarized parliament unable to reach consensus
| Factor | Impact | Political Response |
|---|---|---|
| Protests | Disrupted public services and national strikes | Calls for dialogue and reform |
| Economic Pressure | Heightened public dissatisfaction | Proposed stimulus packages |
| Parliamentary Deadlock | Legislative gridlock | Government reshuffle and leadership changes |
Far-Right Parties Demand Immediate National Elections Amidst Rising Uncertainty
The sudden resignation of France’s prime minister has intensified political instability, creating a vacuum that far-right factions are eager to exploit. Leaders of these parties have issued urgent demands for immediate national elections, arguing that the current government lacks the mandate and stability to navigate the growing economic and social uncertainties. They assert that a fresh electoral mandate is essential to restore public confidence and implement decisive policies aimed at controlling immigration, boosting national security, and revitalizing the economy.
Political analysts observe that the far-right’s push for early polls taps into widespread voter disillusionment, particularly in regions hit hardest by unemployment and inflation. With opposition parties struggling to present a united front, the electoral calendar could be dramatically accelerated, reshaping France’s political landscape within weeks.
| Party | Position on Early Elections | Poll Support (%) |
|---|---|---|
| National Rally | Strongly in favor | 28 |
| Les Républicains | Conditional support | 15 |
| Socialist Party | Opposed | 10 |
| La République En Marche | Undecided | 20 |
Analyzing the Impact of Leadership Changes and Strategic Steps for Political Stability
The recurrent resignation of France’s prime minister signals deep-seated challenges within the current administration, disrupting governance continuity and fostering political uncertainty. This leadership vacuum has emboldened far-right factions to intensify calls for immediate national elections, capitalizing on public discontent and the perceived weakness of centrist parties. Such upheaval not only strains the executive branch but also risks fracturing the parliamentary majority, potentially stalling critical reforms aimed at economic recovery and social cohesion.
To restore stability, strategic measures must prioritize unifying governance and rebuilding public trust. Key steps include:
- Establishing a consensus-driven cabinet that represents diverse political voices and reduces polarization.
- Implementing transparent communication channels to clarify policy intentions and counter misinformation.
- Initiating targeted social programs addressing immediate economic hardships that fuel political unrest.
- Engaging in cross-party dialogues to identify common interests and prevent legislative deadlock.
| Potential Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Government Instability | Coalition-building and power-sharing agreements |
| Public Distrust | Enhanced transparency and regular public briefings |
| Electoral Volatility | Strengthening voter engagement and education |
| Policy Paralysis | Establishing bipartisan committees for critical legislation |
To Wrap It Up
As France navigates yet another political upheaval with the resignation of its prime minister, the calls from the far-right for new national elections underscore the growing tensions within the country’s political landscape. The coming weeks will be critical as President Macron weighs his options amid mounting pressure from opposition parties and public scrutiny. Observers both in France and abroad will be closely watching how the government responds to this latest crisis, which could have lasting implications for the nation’s stability and future direction.