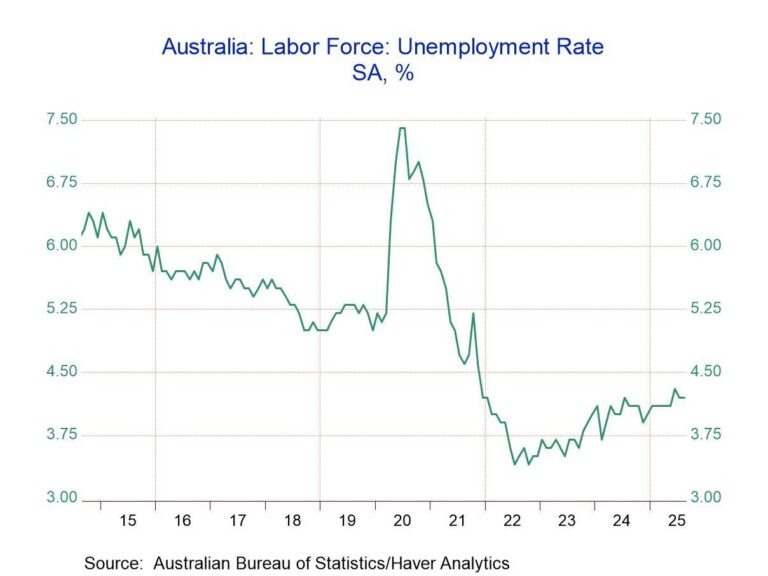
Australia’s unemployment rate has surged to a four-year high, raising fresh concerns about the country’s economic outlook and prompting discussions of a potential interest rate cut. According to official data released on [date], the jobless rate climbed amid softening labor market conditions, challenging policymakers as they weigh efforts to support growth without stoking inflation. The unexpected rise in unemployment has intensified speculation that the Reserve Bank of Australia may reconsider its tightening cycle and shift towards easing monetary policy in the coming months.
Australian Unemployment Reaches Highest Point Since 2020 Amid Economic Challenges
The latest labor market data reveals a significant uptick in unemployment, reaching its highest level since early 2020. This surge has been largely attributed to a combination of persistent inflationary pressures, global supply chain disruptions, and weakening consumer confidence. Key sectors, including hospitality, retail, and manufacturing, have experienced notable layoffs, intensifying concerns about the pace of the economic recovery. Analysts warn that without timely intervention, the jobless rate could rise further, affecting household incomes and spending habits.
In response to these developments, the Reserve Bank of Australia is reportedly reconsidering its monetary policy stance. Market experts suggest that a potential interest rate cut is now back on the table to stimulate job growth and support struggling businesses. The following table summarizes recent unemployment figures alongside forecasted trends:
| Quarter | Unemployment Rate (%) | Forecast (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 2024 | 6.5 | 6.7 |
| Q2 2024 | 6.4 | 6.8 |
| Q3 2024 | 6.6 | 7.0 |
- RBA’s potential rate cut: Aimed at boosting lending and consumer spending.
- Sector-specific impact: Hospitality and retail hardest hit.
- Government stimulus: Calls for renewed support to mitigate job losses.
RBA Considers Interest Rate Cut to Stimulate Job Growth and Enhance Market Stability
The recent spike in unemployment to a four-year high has intensified calls within the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to reconsider its current monetary stance. Officials are weighing the potential benefits of an interest rate cut as a strategic move to invigorate job creation, especially as sectors like retail and hospitality experience sluggish demand. Analysts suggest that a reduction in the cash rate could lower borrowing costs for businesses, encouraging investment and expansion, which in turn could reverse the rising trend of layoffs and underemployment.
Market stability remains a primary concern amid global economic uncertainties and inflationary pressures. The RBA’s cautious approach aims to balance the risks of easing monetary policy against the need to foster a more robust labor market. Key economic indicators influencing the decision include consumer confidence, wage growth, and inflation rates, each presenting mixed signals that complicate policymaking. Below is a snapshot of critical employment data as discussed in recent RBA meetings:
| Indicator | Current Level | Change (YoY) |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment Rate | 5.2% | +0.7% |
| Participation Rate | 66.1% | +0.3% |
| Wage Growth | 2.1% | +0.2% |
| Job Vacancies | 230,000 | -5% |
- Lower rates could stimulate consumer spending.
- Improved credit access might help small and medium enterprises.
- Risks include potential inflation resurgence and currency depreciation.
Experts Advise Targeted Fiscal Policies and Workforce Training to Mitigate Rising Joblessness
Amidst growing concerns over the recent surge in unemployment figures, economic experts stress the importance of strategically targeted fiscal measures to catalyze job growth. Analysts advocate for increased government investment in infrastructure and technology sectors, which are expected to create sustainable jobs. Additionally, they emphasize the need for policies that support small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as these businesses are pivotal for economic resilience and employment generation in local communities.
In parallel, workforce development programs are highlighted as critical in bridging the gap between available jobs and the skills of the unemployed population. Training initiatives focusing on emerging industries such as renewable energy, digital technology, and advanced manufacturing can enhance employability. Below is a brief overview of recommended fiscal actions and workforce strategies:
- Fiscal Actions: Infrastructure funding, SME grants, tax incentives for innovation
- Training Programs: Digital literacy, renewable energy skills, vocational apprenticeships
- Support Mechanisms: Job placement services, career counseling, flexible learning options
| Policy Focus | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Investment | Boost in construction jobs and supply chain demand |
| Workforce Reskilling | Enhanced employability in future growth sectors |
| SME Support Programs | Stabilized job market through business growth |
In Summary
As Australia grapples with its highest unemployment rate in four years, economic policymakers are closely monitoring the situation, with the prospect of an interest rate cut gaining traction. Market watchers and stakeholders alike will be watching upcoming data releases and central bank signals closely, as efforts to support job growth and stabilize the economy take center stage in the months ahead.