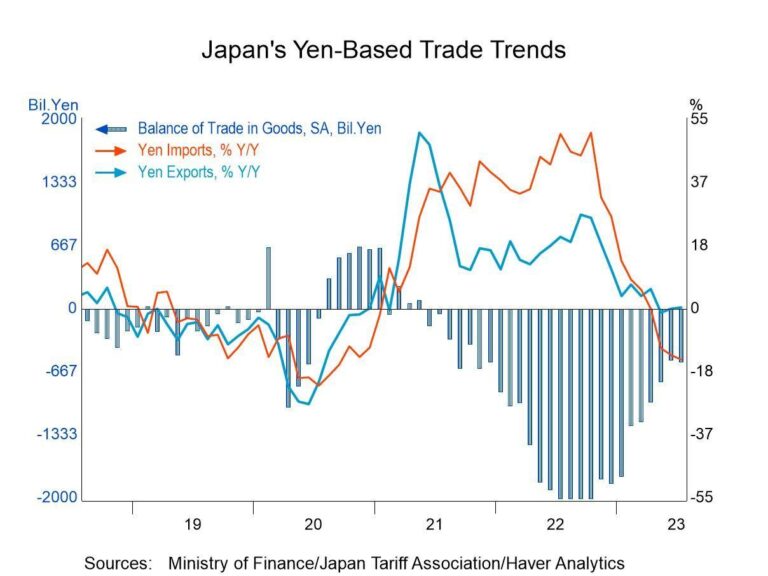
Japan’s exports have experienced a notable decline amid escalating trade tensions with the United States, raising concerns over a potential economic slowdown. According to Bloomberg, the imposition of new US tariffs has disrupted supply chains and dampened demand for Japanese goods, fueling recession fears both domestically and internationally. This development adds pressure to Japan’s fragile economy, which has been striving to regain momentum amid global uncertainties.
Japan’s Export Decline Signals Growing Economic Strain Amid Rising US Tariffs
Japan’s export figures have taken a notable hit this quarter, reflecting the escalating tensions in global trade dynamics. The latest data reveals a 5.8% drop in shipments to the United States, marking the sharpest decline in over a decade. Industry leaders warn this contraction could ripple through the Japanese economy, exacerbating existing vulnerabilities amid stagnating domestic demand and a volatile currency environment. Key sectors such as electronics, automobiles, and machinery-longtime pillars of Japan’s export economy-are facing headwinds due to increased tariffs imposed by Washington.
The fallout from these tariff hikes extends beyond direct trade figures. Analysts caution that the impact will likely deepen supply chain disruptions and raise production costs for Japanese manufacturers. The fallout threatens to:
- Increase input costs, squeezing profit margins
- Slow capital investments as corporate confidence diminishes
- Drive currency fluctuations, complicating export pricing strategies
| Sector | Export Change YoY | Impact Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Automobiles | -7.2% | Tariff increase + Supply chain delays |
| Electronics | -5.1% | Higher input costs + Reduced demand |
| Machinery | -4.5% | US tariffs + Weak global demand |
Impact on Key Industries and Global Supply Chains as Trade Tensions Escalate
The escalation of US tariffs has sent shockwaves through key industries, particularly automotive, electronics, and manufacturing sectors, which form the backbone of Japan’s export economy. Companies are grappling with increased costs of raw materials and components sourced from the US and China, prompting supply chain disruptions and production delays. Japanese automakers, for instance, face the dual challenge of rising tariffs and declining demand in key overseas markets, forcing some to reconsider their global production strategies. Electronics manufacturers, heavily reliant on cross-border supply chains, report bottlenecks that are constraining output and pushing up prices.
Key consequences observed include:
- Supply chain realignment as firms seek alternative suppliers in Southeast Asia and Europe
- Inventory build-ups due to delayed shipments and tariff uncertainties
- Reduced competitiveness of Japanese products in tariff-affected markets
- Heightened volatility in currency markets impacting export pricing
| Industry | Impact | Response |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Cost increases, market contraction | Relocation of some production overseas |
| Electronics | Supply bottlenecks, price pressures | Diversifying suppliers, stockpiling components |
| Machinery | Delayed exports, revenue decline | Negotiating tariff exemptions |
Strategies for Policymakers and Businesses to Mitigate Recession Risks and Restore Growth
To counteract the downward pressure on exports and the resultant economic slowdown, policymakers must adopt a multi-faceted approach. Prioritizing trade diplomacy to negotiate tariff reductions and secure more favorable terms can alleviate immediate costs borne by exporters. Simultaneously, monetary easing combined with targeted fiscal stimulus can bolster domestic demand, cushioning the blow from international trade tensions. Strategic investments in innovation and technology sectors will not only spur productivity but also enhance competitiveness in global markets increasingly influenced by shifting supply chains.
Businesses, on the other hand, need to focus on adaptability and diversification to navigate this turbulent environment. Expanding supply sources beyond the US and exploring emerging markets can mitigate overreliance on any single trade partner. Many companies are accelerating digital transformation and automation to reduce costs and improve efficiency amid shrinking margins. The following table illustrates key strategic priorities for governmental bodies and corporate entities to consider as recession risks heighten:
| Stakeholder | Key Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Policymakers | Trade Diplomacy & Tariff Negotiations | Lower export barriers, stimulate trade flow |
| Policymakers | Monetary & Fiscal Stimulus | Boost domestic consumption and investment |
| Businesses | Supply Chain Diversification | Risk mitigation against geopolitical shocks |
| Businesses | Digital Transformation | Improved efficiency and cost control |
The Conclusion
As Japan grapples with declining exports amid escalating US tariffs, concerns over a potential recession continue to mount. The developments underline the fragile state of global trade and the ripple effects of protectionist policies. Economists and policymakers alike will be closely monitoring the situation, seeking solutions to stabilize Japan’s economy and mitigate broader international fallout.