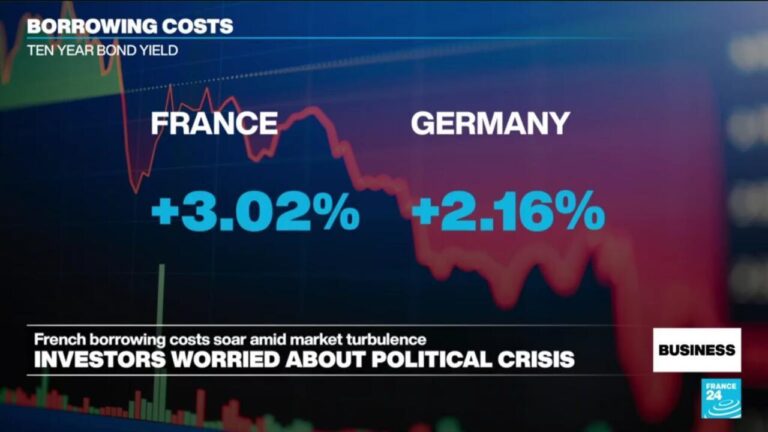
France is confronting the prospect of paying higher borrowing costs than Italy, a development that marks a significant shift in the dynamics of European sovereign debt markets. According to a report by Le Monde.fr, this emerging disparity underscores growing investor concerns about France’s fiscal outlook amid tightening monetary conditions and escalating borrowing needs. The potential for elevated yields on French government bonds compared to those of Italy – traditionally viewed as a riskier borrower – raises questions about market confidence and the broader implications for the eurozone’s economic stability.
France grapples with rising borrowing costs amid market uncertainty
France’s borrowing costs have been on an upward trajectory, fueled by growing market unease and broader eurozone fiscal tensions. Investors are demanding higher yields for French government bonds, reflecting heightened concerns about the country’s debt sustainability amidst slower economic growth forecasts and political uncertainties. Notably, this shift has led to an unusual inversion where France’s borrowing costs are edging closer to, or even surpassing, those of neighboring Italy-a situation that was once considered unlikely given France’s traditionally stronger credit rating and more stable economic fundamentals.
Several factors are influencing this financial dynamic, including:
- Rising inflationary pressures impacting the European Central Bank’s monetary policy outlook.
- Fiscal policy debates in Paris regarding increased government spending versus austerity measures.
- Market volatility driven by geopolitical tensions and uncertainty surrounding energy prices.
| Country | 10-Year Bond Yield | Spread vs Germany (bps) |
|---|---|---|
| France | 3.28% | 75 |
| Italy | 3.25% | 72 |
| Germany | 2.53% | – |
Implications of elevated yields for French fiscal policy and economic growth
Rising sovereign bond yields in France signal mounting pressure on the country’s fiscal strategy. As borrowing costs surpass those of Italy-historically perceived as a riskier debtor-Paris faces the daunting challenge of managing its public debt without stifling economic recovery. The government may be compelled to reconsider its spending priorities, potentially delaying or downsizing investment projects essential for long-term growth. This situation increases debt servicing expenses, forcing policymakers to balance austerity with stimulus to avoid undermining social stability and investor confidence.
Analysts warn that higher yields could slow economic expansion by crowding out private investment, as banks and investors demand greater returns from riskier credit. The ripple effects include:
- Reduced fiscal space for innovation and infrastructure spending
- Heightened vulnerability to external shocks and market volatility
- Potential upward pressure on taxation, impacting consumer and corporate behavior
| Metric | France (2024) | Italy (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| 10-Year Yield | 3.65% | 3.42% |
| Debt-to-GDP Ratio | 112% | 145% |
| Budget Deficit | 3.2% | 4.5% |
Strategies for France to restore investor confidence and manage debt sustainably
To counter rising borrowing costs and reassure markets, France should prioritize fiscal discipline through a combination of expenditure control and revenue enhancement. Streamlining public spending by focusing on efficiency, particularly in social programs and public administration, can curb deficits without stifling growth. Meanwhile, reforming the tax system to broaden the base while eliminating distortive loopholes would strengthen public finances and reduce reliance on volatile revenue streams.
In addition, promoting sustainable economic growth is indispensable to managing debt levels effectively. Key strategies include:
- Encouraging innovation in sectors such as technology and green energy to create new jobs and boost productivity.
- Improving labor market flexibility to attract investment and reduce unemployment.
- Enhancing public-private partnerships to finance infrastructure projects without aggravating public debt.
| Strategy | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Expenditure Control | Reduced budget deficit |
| Tax System Reform | Stable and diversified revenues |
| Innovation Promotion | Long-term economic growth |
| Labor Market Flexibility | Higher employment rates |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Enhanced infrastructure without increasing public debt |
If you’d like, I can also help you refine or expand the content further.
The Way Forward
As France confronts the possibility of higher borrowing costs than Italy, market watchers will closely monitor the evolving dynamics within the eurozone’s debt landscape. The developments underscore growing investor concerns over fiscal discipline and economic stability among Europe’s largest economies. How Paris responds in the coming weeks will be critical not only for its own financial outlook but also for broader confidence in the eurozone’s economic governance.